Generally the federal and state courts in the United States are divided into three main parts:
· Trial Courts
· Intermediate Appellate Courts
· Final Appellate Courts
Federal Courts: the District Courts are the trial courts, where the action is initially filed; the Court of Appeals is the intermediate appellate court; and the Supreme Court is the final appellate court.
· District Courts: are divided into 94 judicial districts. There is at least one district in each state, plus the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico. There are also district courts in the U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, and the Northern Mariana Islands. There are also two specialized courts: the Court of International Trade and the U.S. Court of Federal Claims.
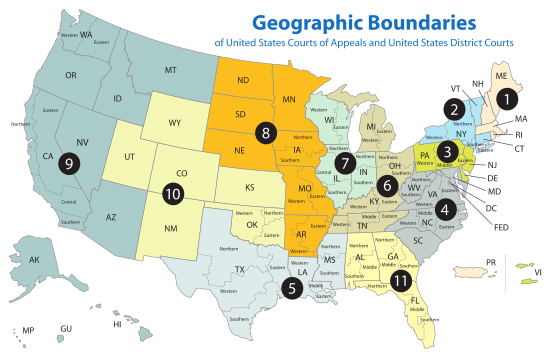
· Court of Appeals: are divided into 12 regional circuits, each encompassing specific judicial districts. The Court of Appeals decisions are binding on the district courts within its circuit. There is also a Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit, which hears appeals from the specialized district level courts (Court of Int’l Trade and U.S. Court of Federal Claims), as well as certain specialized cases, such as patent cases
· Supreme Court: the Supreme Court hears a limited number of cases, at its discretion, which generally involve important questions of federal law. The decisions of the Supreme Court are binding on all federal courts, and are binding on state courts regarding issues of the Constitution and federal law. A case from a state's highest court may be appealed to the Supreme Court if there is a federal legal question involved.
State Courts: also generally have trial courts, intermediate appellate courts, and an appellate court of last resort. Each state uses its own terminology for naming its courts, In New York:
· Supreme Court: unlike in the federal system, the New York trial courts are called the Supreme Courts. There are also the Courts of Claims, the Family Courts, the Surrogate’s Courts, and outside NYC, the County Courts. There are additional trial courts with limited jurisdictions.
· Appellate Division: is the intermediate appellate court in New York. In New York, there are four Appellate Divisions of the Supreme Court, one in each of the State’s four Judicial Departments.
· Court of Appeals: is the highest court in New York State. The Court of Appeals articulates state-wide principles of law, generally focusing on broad issues of law.
http://www.uscourts.gov/uscourts/images/CircuitMap.pdf